DS1318与8051微控制器的接口
发布时间:2010-6-12 10:10
发布者:zealot
本应用笔记演示了使用DS1318历时计数器计算天数。软件实例中包括基本的操作程序,并给出了应用电路的原理图。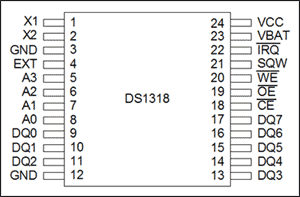
计数器概述 该应用笔记演示了如何使用DS1318历时计数器,DS1318具有44位计数器,可提供244μs的计时分辨率。44位计数器通过6个8位寄存器(图1)进行访问。 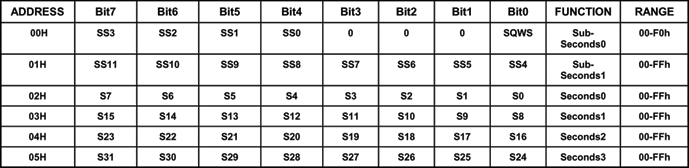
从概念上来说,44位计数器可以分成一个12位亚秒级计数器和一个分辨率为一秒的32位计数器(图2)。如果应用种不需要亚秒级分辨率,则可访问32位秒计数器。 
在本应用笔记提供的示例中,软件子程序每秒一次连续读取32位秒计数器的数值,并通过8051微控制器(μC)的UART接口以ASCII码格式输出时间和日期。时间和日期基于从1970年1月1日,00:00:00起所经历的时间,单位为秒。00000000h对应的时间是1970年1月1日,00:00:00;42C924C0h对应的时间为2005/7/4 12:00:00。 另一子程序将器件配置成频率为1Hz的周期性中断,每次发生中断,中断处理程序读取计数器数据,将时间转换成日期格式,并通过URAT以ASCII格式输出数据。 我们还提供其它例程,在其它例程中可以对DS1318进行以下操作:可以将用户输入数据写入寄存器;将用户输入的时间和日期转换成自1970年1月1日起所经历的时间,单位为秒;向计数器写入数据。另一子程序用于读取DS1318寄存器,并以十六进制格式输出数据。 工作原理 本应用笔记中的硬件电路将DS1318的数据放入μC的数据存储空间。μC通过读、写正确地址的数据存储器访问DS1318寄存器。 本实例中采用DS80C323低电压、8051兼容微控制器。用户输入数据和程序输出数据都将传递到μC,通过PC终端仿真器的RS-232接口进行通信。有关本应用笔记中DS80C323微控制器的详细信息可从公司网站下载。 程序如下: Figure 3. Program Listing /*********************************************************************/ /* Ds1318AN.c program, use on the DS1318 app note board */ /*********************************************************************/ #include #include #include /***************************** Defines *******************************/ #define SSEC1 XBYTE[0x0000] #define SSEC2 XBYTE[0x0001] #define SEC0 XBYTE[0x0002] #define SEC1 XBYTE[0x0003] #define SEC2 XBYTE[0x0004] #define SEC3 XBYTE[0x0005] #define AL0 XBYTE[0x0006] #define AL1 XBYTE[0x0007] #define AL2 XBYTE[0x0008] #define AL3 XBYTE[0x0009] #define CTLA XBYTE[0x000A] #define CTLB XBYTE[0x000B] #define STAT XBYTE[0x000C] /************************* bit definitions ***************************/ /************************* Global Variables **************************/ uchar int_flg = 0; /*********************** Function Prototypes *************************/ void init_rtc(); void writebyte(); void readregs(); void disp_clk_regs(); void disp_clk_regs_int(); void bin2date(); unsigned long date2bin(uint, uint, uint, uint, uint, uint); void external0_int(void); void init_rtc() /* ------------ set the time and date ----------------- */ /* Note: NO error checking is done on the user entries! */ { uint yrs, mon, dt, hrs, min, sec; unsigned long y; printf("\nEnter the year (1970-2099): "); scanf("%d", &yrs); printf("Enter the month (1-12): "); scanf("%d", &mon); printf("Enter the date (1-31): "); scanf("%d", &dt); printf("Enter the hour (0-23): "); scanf("%d", &hrs); printf("Enter the minute (0-59): "); scanf("%d", &min); printf("Enter the second (0-59): "); scanf("%d", &sec); CTLA = 0x46; /* disable update transfers */ y = date2bin(yrs, mon, dt, hrs, min, sec); SEC0 = (y & 0xff); SEC1 = ((y >> 8) & 0xff); SEC2 = ((y >> 16) & 0xff); SEC3 = ((y >> 24) & 0xff); CTLA = 0xC6; } void writebyte() /* -------- enter data for one byte --------- */ { int add; uchar dat; printf("\nEnter address (hex): "); scanf("%x", &add); printf("Enter data (hex): "); scanf("%bx", &dat); XBYTE[add] = dat; } void readregs() /* --------- list all of the registers -------- */ { uchar inc; CTLA = 0x46; /* disable update transfers */ printf("\n"); for(inc = 0; inc < 0xd; inc++) { printf("%02bx ", XBYTE[inc]); } CTLA = 0xC6; /* enable transfers, osc, sqw */ } void disp_clk_regs() /* -------------- read time & date using TE as intended ----------------- */ { uchar prv_sec = 99; while(!RI) /* Read & Display Clock Registers */ { if(prv_sec != SEC0) /* display once per second */ { bin2date(); prv_sec = SEC0; } } RI = 0; /* Swallow keypress to exit loop */ } void disp_clk_regs_int() /* ----- display time using irq output ----- */ { CTLA = 0xC6; /* enable update transfers, oscillator, squarewave and PIE */ CTLB = 0xA0; /* PF = 1Hz, SQW = 32kHz */ EX0 = 1; /* enable interrupt 0 */ IT0 = 1; /* edge activated */ PX0 = 0; /* low priority */ EX1 = 0; /* disable interrupt 1 */ EA = 1; /* enable all interrupts */ while(!RI) /* Read & Display Clock Registers */ { while(!int_flg); /* wait for interrupt */ if(int_flg & 0x02) /* only display if the periodic flag caused the interrupt */ { EX0 = EX1 = 0; /* disable interrupts while updating the display */ bin2date(); /* calculate and display time and date */ int_flg = 0; /* for this example, we'll just clear all interrupt sources */ EX0 = EX1 = 1; /* re-enable interrupts */ } } EX0 = 0; /* disable interrupt */ RI = 0; /* Swallow keypress to exit loop */ } /* Note: The following routine could be replaced with the ANSI C ctime function */ void bin2date() /* ------ convert binary time to date format ------ */ { int yrs, mon, day, date, dow, tmp, jday, hrs, min, sec; uchar ssec; unsigned long x, j, n; CTLA = 0x46; /* disable update transfers */ x = SEC3; x <<= 8; x |= SEC2; x <<= 8; x |= SEC1; x <<= 8; x |= SEC0; ssec = SSEC2; CTLA = 0xC6; /* enable transfers, osc, sqw */ j = x / 60; /* whole minutes since 1/1/70 */ sec = x - (60 * j); /* leftover seconds */ n = j / 60; min = j - (60 * n); j = n / 24; hrs = n - (24 * j); j = j + (365 + 366); /* whole days since 1/1/68 */ day = j / ((4 * 365) + 1); tmp = j % ((4 * 365) + 1); if(tmp >= (31 + 29)) /* if past 2/29 */ day++; /* add a leap day */ yrs = (j - day) / 365; /* whole years since 1968 */ jday = j - (yrs * 365) - day; /* days since 1/1 of current year */ if(tmp <= 365 && tmp >= 60) /* if past 2/29 and a leap year then */ jday++; /* add a leap day */ yrs += 1968; /* calculate year */ for(mon = 12; mon > 0; mon--) { switch(mon) { case 1: tmp = 0; break; case 2: tmp = 31; break; case 3: tmp = 59; break; case 4: tmp = 90; break; case 5: tmp = 120; break; case 6: tmp = 151; break; case 7: tmp = 181; break; case 8: tmp = 212; break; case 9: tmp = 243; break; case 10: tmp = 273; break; case 11: tmp = 304; break; case 12: tmp = 334; break; } if((mon > 2) && !(yrs % 4)) /* adjust for leap year */ tmp++; if(jday >= tmp) break; } day = jday - tmp + 1; /* calculate day in month */ dow = (j + 1) % 7 + 1; /* 1 = Sun, 2 = Mon, and so on */ printf("\n%04d/%02d/%02d %d %02d:%02d:", yrs ,mon, day, dow, hrs, min); printf("%02d.%02bu", sec, ssec); } /* ---- convert date to elapsed days in binary ---- */ unsigned long date2bin(uint yrs, uint mon, uint day, uint hrs, uint min, uint sec) { unsigned long x; /* the following is broken down for clarity */ x = 365 * (yrs - 1970); /* calculate number of days for previous years */ x += (yrs - 1969) >> 2; /* add a day for each leap year */ if((mon > 2) && (yrs % 4 == 0)) /* add a day if current year is leap and past Feb 29th */ x++; switch(mon) { case 1: x += 0; break; case 2: x += 31; break; case 3: x += 59; break; case 4: x += 90; break; case 5: x += 120; break; case 6: x += 151; break; case 7: x += 181; break; case 8: x += 212; break; case 9: x += 243; break; case 10: x += 273; break; case 11: x += 304; break; case 12: x += 334; break; } x += day - 1; /* finally, add the days into the current month */ x = x * 86400; /* and calculate the number of seconds in all those days */ x += ((long) hrs * 3600); /* add the number of seconds in the hours */ x += (min * 60); /* ditto the minutes */ x += sec; /* finally, the seconds */ return(x); } void external0_int(void) interrupt 0 /* --- display time/date on interrupt from RTC --- */ { EX0 = EX1 = 0; /* disable interrupt */ int_flg = STAT; /* clear the interrupt source, save the info */ STAT = 0; /* clear PF (and all other bits) */ EX0 = EX1 = 1; /* re-enable interrupt */ } main (void) /* ----------------------------------------------------- */ { uchar i, M, M1; while (1) { printf("\nDS1318 build %s\n", __DATE__); printf("CI Clock Init CN Clk iNt rd\n"); printf("CR Read Time W Write byte\n"); printf("R Read regs\n"); printf("Enter Menu Selection:"); M = _getkey(); switch(M) { case 'C': case 'c': printf("\rEnter Clock Routine to run: C"); M1 = _getkey(); switch(M1) { case 'I': case 'i': init_rtc(); break; case 'N': case 'n': disp_clk_regs_int(); break; case 'R': case 'r': disp_clk_regs(); break; } break; case 'R': case 'r': readregs(); break; case 'W': case 'w': writebyte(); break; } } } 电路原理图见PDF附件。  4.pdf
(29.53 KB)
4.pdf
(29.53 KB)
|






网友评论